The Human Lymphatic System
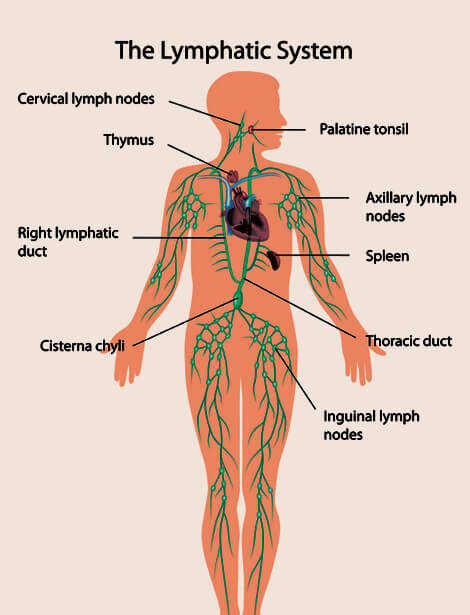
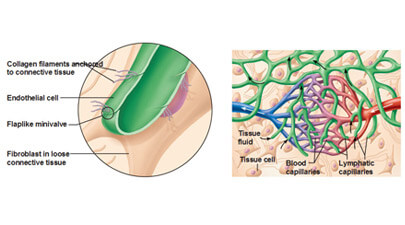
Carrying a clear fluid directly towards the pumping organ, heart, it consists of a network of tubes. These tubes are called lymphatic vessels, while the clear fluid contained in them is known as lymph. Concerning the etymology of the word "lymph", it has been derived from a Latin word "lympha", which is the name of "water goddess". To put it in simple words, you can say that lymph is essentially recycled blood plasma. In an adult human, nearly 20 liter of blood is processed, on daily basis, through the mechanism of capillary filtration in which blood plasma is removed and only blood cells are left behind. About 17 liter of this blood plasma is reabsorbed directly into the blood vessels, while the remaining 3 liter is returned to the circulatory system with the help of lymphatic system. So, the primary function of this system is to serve as an accessory route for the delivery of the excess interstitial fluid back to the blood circulatory system.
As lymphatic system helps and facilitates the circulatory system in collecting back the blood plasma (or interstitial fluid), the former is usually termed as an integral part of the latter. However, it also has a considerable overlap with the lymphoid system and significantly contributes to the working of the immunity in your body.
For the proper understanding of the overlap of these two systems, you can take example of the lymph nodes which are also found to contain lymphoid tissues. So far as the discovery of lymphatic system is concerned, it was first described in the 17th century independently by a Swedish scientist, Olaus Rudbeck, and Danish physician, Thomas Bartholin.
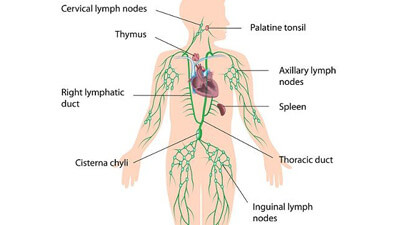
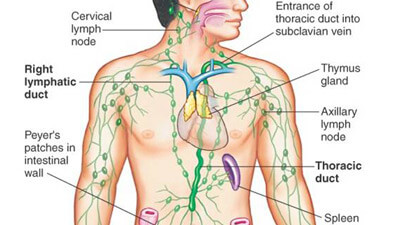
There are three major parts of lymphatic system, namely, lymph vessels, lymph nodes and lymph. In composition, this clear watery fluid also contains salts, glucose, urea, protein molecules and some other substances which are carried throughout the body. The functions of this accessory circulatory mechanism include: the removal of interstitial fluid from the tissues; transportation of white blood cells to and from the lymph nodes into the bones; and absorption and transport of fatty acids & fats (as chyle) from the digestive system.
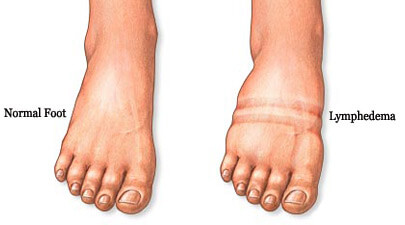
Lymphedema, Hodgkin’s lymphoma, lymphangiomatosis and lymphangiosarcoma are some of the prevailing lymphatic system diseases. To get more understanding of the topic, “What is Lymphatic System?” read other related material as well: "Parts of Lymphatic System"; "Functions of Lymphatic System"; Facts about Lymphatic System"; and "Diseases of Lymphatic System".
Informative Articles About "Human Lymphatic System"
Parts Of Lymphatic System
Owing to intimacy and certain functional similarities, lymphatic system is rightly considered a part of the circulatory ...
Functions Of Lymphatic System
Human lymphatic system works as an accessory and complementary mechanism for the proper execution of the functions assigned ...
Diseases Of Lymphatic System
The malfunctioning or damage to any part of the lymph circulation ...
Lymphatic System Facts
Lymphatic system works in coordination and collaboration with ...